Engagement and Wedding Rings - Choosing the Stones
Diamonds
An Independent Diamond Grading Certificate.
If you are buying a diamond over 0.5cts then we strongly recommend getting a stone that comes with an grading report. Usually, the stones we source will come with a GIA or equivalent certificate. This ensures you know what you are buying and have documented values in terms of carat weight, color, clarity, and cut. Diamond certificates are issued by an independent gemological laboratory. These laboratories don’t sell diamonds and have no connection to diamond mines, dealers or retailers, so they have no vested interest in the grade they give a diamond. They use diamond graders and gemologists who undergo intensive training and several graders evaluate an individual diamond separately. Because no two diamonds are exactly alike, the graders reach a consensus to make sure the grade they assign is accurate, consistent and reliable. However, this is not a valuation of the stone and will not give you a $$ value as to it's price/worth.
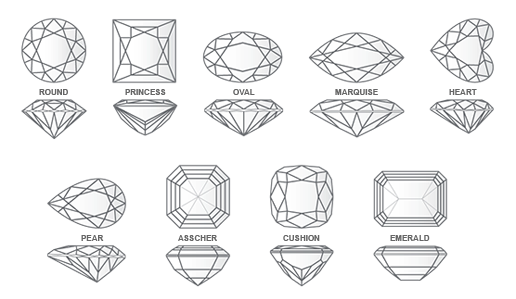
Common Diamond Shapes
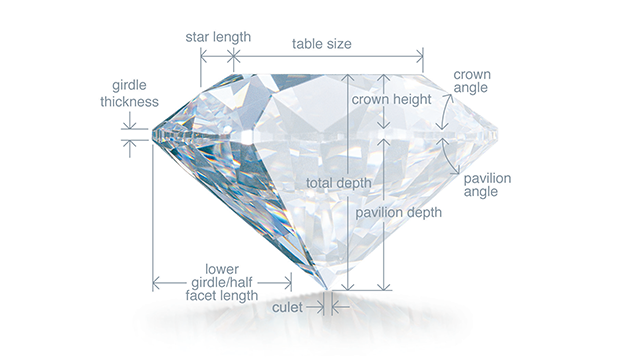
Cut
A diamond's cut is crucial to the stone's final beauty and value. Though extremely difficult to analyze or quantify, the cut of any diamond has three attributes: brilliance (the total light reflected from a diamond), fire (the dispersion of light into the colors of the spectrum), and scintillation (the pattern of light and dark areas and the flashes of light, or sparkle, when a diamond is moved).
The distance from the bottom of the girdle to the culet is the pavilion depth. A pavilion depth that's too shallow or too deep will allow light to escape from the side of the stone or leak out of the bottom. A well-cut diamond will direct more light through the crown.
This means that a well cut diamond will really "sparkle" and "shine". A poorly cut diamond will be too shallow or too deep affecting the reflections, diameter and setting of the stone; and stone with girdles too thick or too thin will be difficult to secure in the setting.
The distance from the bottom of the girdle to the culet is the pavilion depth. A pavilion depth that's too shallow or too deep will allow light to escape from the side of the stone or leak out of the bottom. A well-cut diamond will direct more light through the crown.
This means that a well cut diamond will really "sparkle" and "shine". A poorly cut diamond will be too shallow or too deep affecting the reflections, diameter and setting of the stone; and stone with girdles too thick or too thin will be difficult to secure in the setting.
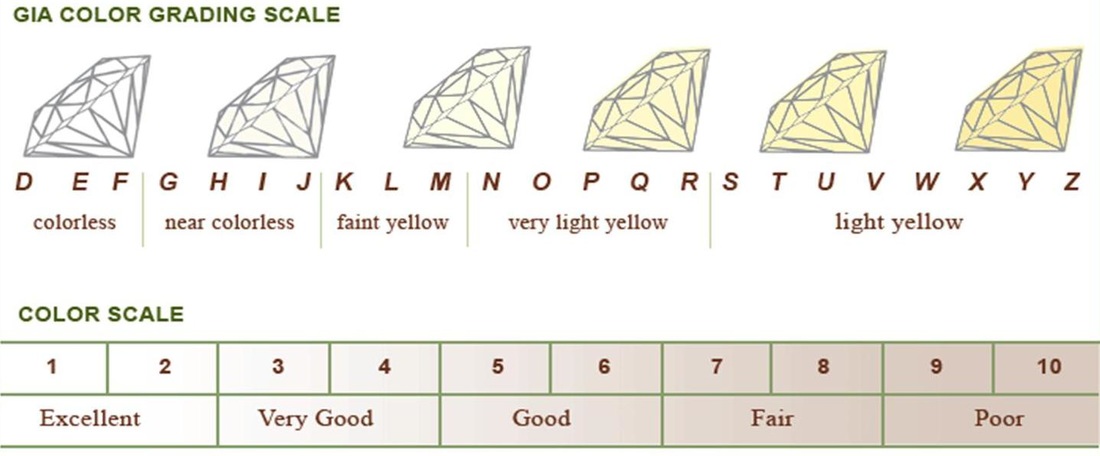
Colour
The diamond color evaluation of most gem-quality diamonds is based on the absence of color. A chemically pure and structurally perfect diamond has no hue, like a drop of pure water, and consequently, a higher value. GIA's D-to-Z diamond color-grading system measures the degree of colorlessness by comparing a stone under controlled lighting and precise viewing conditions to masterstones of established color value.
GIA's diamond D-to-Z color-grading scale is the industry's most widely accepted grading system. The scale begins with the letter D, representing colorless, and continues, with increasing presence of color, to the letter Z.
Many of these color distinctions are so subtle that they are invisible to the untrained eye; however, these distinctions make a very big difference in diamond quality and price.
I usually recommend main diamonds be between E to G, and side/small diamonds be F to H. I find that grades beyond this will loose their "sparkle" and look "dull" very quickly as they get dust and dirt build-up. A clean will restore them but a "whiter" stone will look "white" even with dirt and dust.
GIA's diamond D-to-Z color-grading scale is the industry's most widely accepted grading system. The scale begins with the letter D, representing colorless, and continues, with increasing presence of color, to the letter Z.
Many of these color distinctions are so subtle that they are invisible to the untrained eye; however, these distinctions make a very big difference in diamond quality and price.
I usually recommend main diamonds be between E to G, and side/small diamonds be F to H. I find that grades beyond this will loose their "sparkle" and look "dull" very quickly as they get dust and dirt build-up. A clean will restore them but a "whiter" stone will look "white" even with dirt and dust.
Fancy Coloured Diamonds
Fancy-colour diamonds are either yellow or brown diamonds that have more color than a Z masterstone or they exhibit a color other than yellow or brown. Champagne, yellow, brown and black cost a little more than quality white diamonds, where pink, red, green, purple and blue diamonds are very rare and costly.
Fancy-colour diamonds are either yellow or brown diamonds that have more color than a Z masterstone or they exhibit a color other than yellow or brown. Champagne, yellow, brown and black cost a little more than quality white diamonds, where pink, red, green, purple and blue diamonds are very rare and costly.
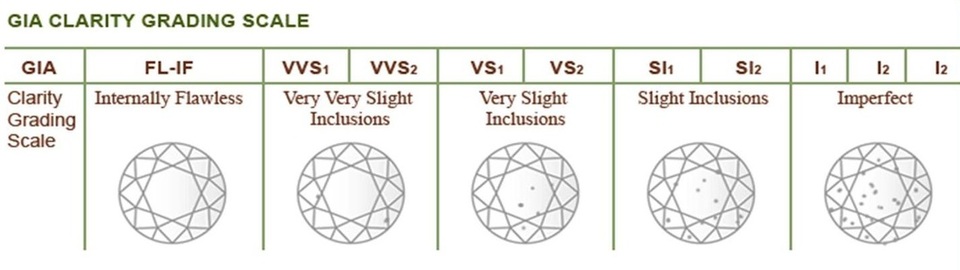
Clarity
Diamond Clarity refers to the absence of inclusions (internal ) and blemishes (external). Natural diamonds are the result of carbon exposed to tremendous heat and pressure deep in the earth. Evaluating diamond clarity involves determining the number, size, relief, nature, and position of these characteristics, as well as how these affect the overall appearance of the stone. While no diamond is perfectly pure, the closer it comes, the higher its value.
I personally don't think you need a flawless diamond - the naked eye won't notice very slight inclusions and it won't detract from a diamond's shine and brilliance. However, slight inclusions and imperfections are more noticeable and may put the diamond at risk of fractures and chips.
I personally don't think you need a flawless diamond - the naked eye won't notice very slight inclusions and it won't detract from a diamond's shine and brilliance. However, slight inclusions and imperfections are more noticeable and may put the diamond at risk of fractures and chips.
Carats
Diamond carat weight is the measurement of how much a diamond weighs. Each carat can be subdivided into 100 'points.' For instance, the jeweler may refer to a diamond that weighs 0.25 carats as a 'twenty-five pointer.' Diamond weights greater than one carat are expressed in carats and decimals. Because it a measurement of weight, different cut diamonds, all of the same carat weight can be different sizes.
Gemstones
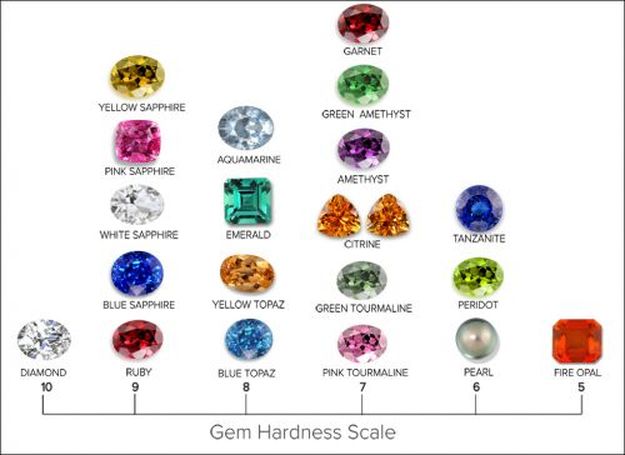
When thinking about a coloured gemstone Ring - Cut, Colour, Clarity and Cararts are also important. However, the most important is Hardness. Ie, the hardness or softness of the gemstone - it's ability to be scratched or chipped. Diamonds are the hardest stones - making them ideal for everyday wear and long-lasting value. Gemstones range in hardness and care must be taken when choosing - I usually don't recommend a stone less than "7" on the Mohs scale unless you are prepared to take your rings off for sports, cleaning, manual labour etc.
Hardest (8.0-10.0) Spinel, Topaz, Alexandrite, Emerald, Ruby, Sapphire & Diamond
Medium (7.0 - 7.5) Amethyst, Citrine, Quartz, Tormaline, Aquamarine, Garnet, Zircon
Soft Stones (6.0-6.5) Jade, Labradorite, Moonstone, Opal, Agate, Kunzite, Tanzanite, Peridot
Medium (7.0 - 7.5) Amethyst, Citrine, Quartz, Tormaline, Aquamarine, Garnet, Zircon
Soft Stones (6.0-6.5) Jade, Labradorite, Moonstone, Opal, Agate, Kunzite, Tanzanite, Peridot